00:00
A Global Healthcare Revolution in Every Heartbeat:
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the world’s leading cause of death, responsible for approximately 18 million deaths each year—nearly one-third of all global deaths. Each year, an estimated 15 to 20 million people suffer heart attacks worldwide, and about 10–15% of those are fatal, depending on access to care and region-specific healthcare infrastructure. However, technology is changing the equation. From AI-powered implants to smart diagnostics and predictive digital twins, a new generation of medical devices is reshaping the treatment landscape—delivering earlier detection, personalised therapy, and smarter follow-up care.
1. Implantable Cardiac Devices: Precision Inside the Body
Adaptive Pacemakers & ICDs
Modern cardiac devices are now ‘self-learning’. Advanced pacemakers and defibrillators automatically fine-tune themselves based on real-time patient feedback, adjusting pacing and shock thresholds with AI-assisted logic. These technologies help stabilise heart rhythms more effectively while reducing unnecessary interventions and emergency visits.
Hemodynamic Monitors: CardioMEMS and Beyond
The CardioMEMS device, a wireless pulmonary artery pressure monitor, is showing remarkable results. In trials involving over 1,300 patients, it reduced heart failure–related hospitalisations by 36% within the first 12 months. New European data confirms similar effectiveness in diverse populations, enabling earlier clinical intervention and fewer emergency admissions.
AI-Enhanced Loop Recorders
Implantable cardiac monitors—known as loop recorders—now use AI to filter ECG data and reduce false positives. One study showed a 60% reduction in non-actionable alerts, saving nearly $30,000 per 600 patients annually and hundreds of hours in clinician review time.
2. Connected Care: Monitoring from Anywhere
Wearables with Clinical Precision
Wearable medical devices like AliveCor’s KardiaMobile or Eko’s smart stethoscope detect abnormal heart rhythms with FDA-cleared accuracy. These tools go beyond fitness tracking, offering real-time detection of atrial fibrillation and heart failure indicators—delivering hospital-grade ECG data to a clinician’s dashboard.
Home-Based Heart Failure Surveillance
AI-powered home monitoring systems collect data on blood pressure, heart rate, weight, and breathing. These systems, paired with machine learning, can predict decompensation and allow clinicians to adjust therapy proactively. Results show up to a 25% reduction in hospital readmissions and millions saved in preventable care costs.
Continuous Arrhythmia Detection
Patch-based ECG devices worn for days or weeks can detect silent arrhythmias. With AI assistance, these tools reduce data overload and ensure that clinically relevant events are flagged faster, enabling swift intervention in high-risk patients.
3. Smart Pills and Medication Adherence
Digital pills with ingestible sensors are a new frontier in cardiac medication adherence. These tablets signal when they’ve been swallowed, sending data to clinicians and apps. Early trials show:
– Over 97% adherence rates
– Significantly fewer missed doses in chronic heart patients
– Reduced risk of stroke and secondary cardiac events in hypertension and anticoagulation therapy
Regulators like the European Medicines Agency now recognise these systems as valid biomarkers for medication adherence.
4. AI-Driven Imaging & Diagnostics
AI-Enhanced ECG Interpretation
AI-trained models can analyse subtle ECG patterns invisible to the human eye, predicting heart failure, arrhythmias, and even long-term mortality risk. Research shows:
– 79% accuracy in predicting future heart failure
– 78% accuracy in 10-year mortality risk estimation
These models are now being trialled in hospitals across the UK, the US, and Asia, radically transforming point-of-care diagnostics.
Automated CT & MRI Analysis
AI accelerates analysis of coronary CT angiograms, echocardiograms, and MRIs. Algorithms now identify arterial plaques, valve dysfunction, and pumping inefficiencies within seconds. This translates into:
– Faster emergency decision-making
– Fewer diagnostic errors
– Earlier detection of coronary artery disease
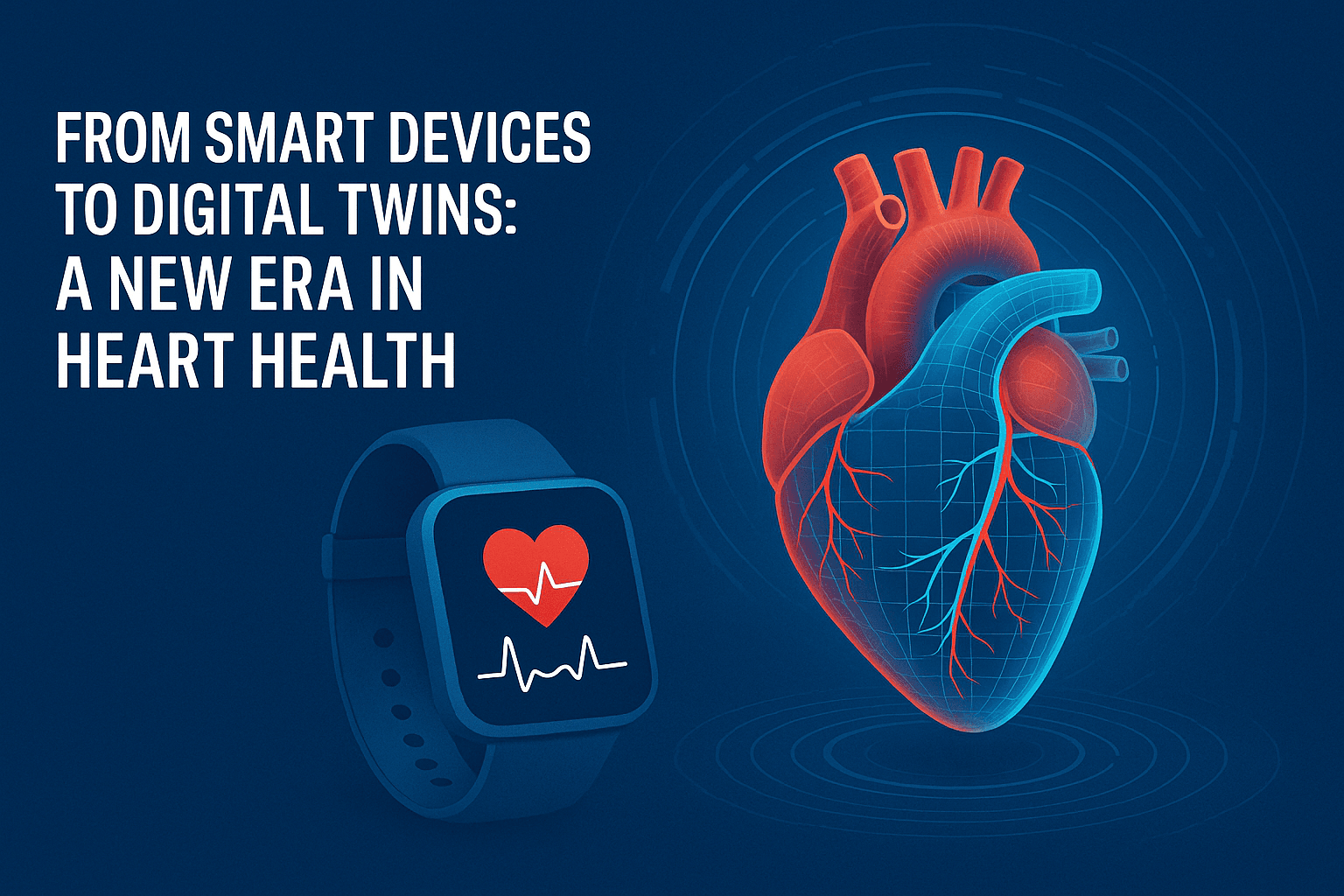
5. Digital Twins & Predictive Analytics: Your Virtual Heart in High Definition
Imagine a virtual version of your heart—a digital twin—that mirrors its structure, function, and disease progression in real time. This isn’t science fiction; it’s emerging as a powerful tool to transform cardiovascular care.
What Are Digital Twins?
A digital twin is a comprehensive, data-driven simulation of an individual’s heart, continuously updated with clinical data, imaging, and wearable inputs. This replica mimics real-life physiology and can be used to test interventions digitally before applying them to the patient.
How They Work:
1. Data Fusion: Combines imaging (e.g., MRI, CT), ECG, wearable data, genetics, and lifestyle.
2. AI & Biomechanical Modelling: Merges machine learning with physics-based simulations for accurate heart dynamics.
3. Continuous Syncing: Maintains real-time mirroring of the patient’s evolution through cloud or edge computing.
4. Predictive Testing: Enables clinicians to run “what-if” scenarios, adjusting medications or simulating device placements without risk.
Proven Applications:
A. Population-Scale Twin Modelling
A 2025 study built 3,820 cardiac digital twins from UK Biobank participants and ischaemic heart disease cohorts. These twins revealed how heart conduction and tissue mechanics vary by age and sex, and obesity and correlate with cardiovascular outcomes.
B. Johns Hopkins Arrhythmia Simulation
A clinical trial at Johns Hopkins created personalised digital hearts using patient MRI scans to simulate arrhythmia ablation. The predictions aligned closely with actual surgical outcomes, highlighting the potential to guide interventions before a scalpel is used.
C. Mixed Reality Surgical Planning
A Norwegian study used digital twins visualised via mixed reality during paediatric cardiac surgery. The holographic models led to changes in surgical strategy in 68% of cases, improving anatomical understanding and guiding better planning.
Market & Momentum:
The global healthcare digital twin market reached US$ 1.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to US$ 21 billion by 2028, fuelled by massive investments from governments, startups, and institutions.
Why Digital Twins Matter Now:
– Personalised Prediction: Tailored treatment plans based on individual heart behaviour.
– Safer Decisions: Simulate procedures virtually before applying them.
– Accelerated Innovation: Pharma trials can run simulations for faster and safer development.
– Disease Monitoring: Detect subtle changes early and adjust therapy proactively.
Challenges:
– Complex Data Integration: Requires seamless and secure data pipelines.
– Validation Requirements: Needs rigorous clinical outcome comparisons.
– Ethical and Privacy Considerations: Real-time, sensitive data must be handled carefully.
– Adoption Barriers: Requires new digital infrastructure and clinical upskilling.
The Bottom Line:
Digital twins represent the apex of personalised cardiovascular care—merging data, AI, and simulation into an ultra-precise tool for diagnosis, treatment planning, and therapy optimisation. From population models to surgical guidance, they’re already saving time, costs, and lives.
6. Emerging Innovations on the Horizon
The medtech pipeline is more exciting than ever. Among the most promising developments:
– Micropacemakers powered by body heat—no batteries needed
– Biointelligent stents that release drugs based on tissue feedback
– Transparent skin patches monitoring ECG, hydration, and chemistry
– AI-integrated implantables offering cloud-based diagnostics and live alerts
Together, these innovations could create a closed-loop cardiovascular ecosystem that continuously senses, thinks, and responds to patient needs.
7. The Impact by the Numbers
The Problem (Annually):
– 18 million global cardiovascular deaths
– 805,000 heart attacks in the U.S.
– 10–15% fatality rate for acute cardiac events
The Opportunity:
– AI and device-based early detection could prevent up to 20–30% of future heart attacks
– Remote monitoring and AI-adjusted medication can reduce hospital readmissions by 25% and mortality by 15–45%
– Adherence monitoring with smart pills can push compliance rates above 95%, reducing adverse events and stroke risks
The Projection:
– 3 to 4 million heart attacks could be prevented each year
– Up to 5 to 8 million lives could be saved annually
– Billions in avoidable healthcare costs could be redirected toward preventive and personalised care
8. Final Thoughts and Next Steps
A New Standard of Heart Care Is Here
Technology is not just improving heart care—it’s rewriting the rulebook. We’re entering an era where:
– Heart attacks can be predicted
– Cardiac events can be intercepted
– Medications can be monitored in real time
– Treatment plans can be simulated before they’re even prescribed
This is not a distant vision—it’s happening now. With real devices, real data, and real results.
What Comes Next: A Call to Action
To make this easily available globally, the healthcare ecosystem must unite:
– Pharma: Innovate drug-device combinations that offer clinical feedback, adherence support, and patient-centric outcomes
– Hospitals: Integrate AI and remote platforms into standard CVD protocols
– Regulators: Accelerate approvals for validated AI tools and real-world performance monitoring
– Tech Firms: Focus on interoperability, affordability, and clinician usability
It’s inspiring to see how AI and smart medical devices are transforming cardiovascular care around the world. The future of healthcare is rooted in proactive, personalised, and data-driven solutions—ones that place the patient at the centre.
For businesses, researchers, and technology developers, this represents an incredible opportunity to build new ecosystems of care that are predictive rather than reactive. Whether you’re in pharmaceuticals, medtech, or health IT, the message is clear: the convergence of AI and clinical science is not just a possibility—it’s a responsibility.
The future of heart health is within reach, and with collaboration, innovation, and a shared purpose, we can make it accessible to all.